Objectives
The goal of our research project is to instal a modular platform for testing light hybrid-electric vehicles (HEV) by using the Hardware-in-the-Loop (HiL) concept. The elements which are under study here are the propulsion and the main auxiliaries (steering, ventilation and braking systems). The hybrid character of the vehicle is at power suply level, meaning that we will test the HEV’s suply based on battery and ultracapacitor; also, the use of fuel cell suply can be taken into consideration.
The modular character of the platform is seen at all levels of the power train: the supply (we will be able to test different types of batteries, ultracapacitors, of different materials and configurations – even fuel cells could be integrated in our testing platform), the controller (which contains the control unit and the power converter – function of the electrical machine type we will have different power static converters) and the motorization (high speed and low speed structures could be integrated, as well as the with-transmission or without-transmission – in-wheel – variants; also, the magnetic or mechanical gear, with different gear ratios could be integrated).
Another degree of modularity will be applied to the auxiliaries. Based on a programmable power load we could consider a generic auxiliary consumer, which will be consider as a global consumer, or we will consider real auxiliaries, for a lower voltage level, like the auxiliaries, ventilation and braking systems, to which we could add others – like the compressor for fuel cells, micromotors for electric windows and sits etc.
In order to explain the main energy flow in our testing platform see figure below, where the motorization and the main studied auxiliaries are considered.
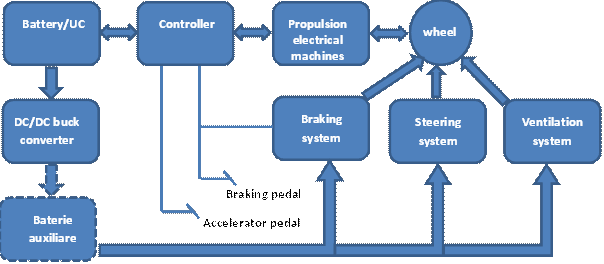
(A supplementary battery, of low voltage, could be used for auxiliaries, especially since their presence, when the amount of installed power is increased, could affect the vehicle’s authonomy.)
Duet o budget rectification and time implementation extension, the implementation of the research objectives will be made based on the following table:
|
Phase no. |
Phase title |
Involved partners |
Start month (1 ... n-1) |
End month (2 ... n) |
|
1 |
Establishing the modular architecture of the HEV and the main elements of the system. |
CO, P1, P2 |
July 2012 |
December 2012 |
|
2 |
Study of the motorization and of the auxiliary subsystems of the HEV. |
CO, P1, P2 |
January 2013 |
December 2013 |
|
3 |
Study of the control of the motorization and of the auxiliaries and power source modelling. |
CO, P1, P2 |
January 2014 |
December 2014 |
|
4 |
Study of the energy management with high efficiency and reliability on board of the HEV. |
CO, P1, P2 |
January 2015 |
December 2015 |
|
5 |
Software modeling of the entire platform and the implementation of the HiL on the build system. |
CO, P1, P2 |
January 2016 |
June 2016 |
At project proposal (July 2012), the following objectives have been declared:
|
Phase no. |
Phase title |
Involved partners |
Start month (1 ... n-1) |
End month (2 ... n) |
|
1 |
Establishing the modular architecture of the HEV and the main elements of the system. |
CO, P1, P2 |
July 2012 |
December 2012 |
|
2 |
Study on HEV’s motorization and auxiliaries: steering, braking, air-conditioning system. |
CO, P1, P2 |
January 2013 |
December 2013 |
|
3 |
Study of a highly efficient and reliable energy management of the HiL platform for the HEV. |
CO, P1, P2 |
January 2014 |
December 2014 |
|
4 |
Software modeling and validation of the performances of the modular HiL platform of the HEV. |
CO, P1, P2 |
January 2015 |
June 2015 |
These objectives will be integrated into the project phases given subsequent, as well as their related activities.
